Fur Seals Suppress REM Sleep for Very Long Periods without a Subsequent Rebound
By Meagan Ando, SRC intern
There are two sleep states that all mammals and birds utilize: slow-wave sleep (SWS) and rapid eye movement (REM). REM sleep is vital to the psychological and physical well-being of living organisms. Extended periods of deprivation can cause severe dysfunction and can even lead to death (Kushida, C. A. et. al., 1989). The northern fur seal (Callorhinus ursinus) can go many days or even weeks with prolonged REM sleep deprivation as they travel through ocean waters. In general, with extended periods of non-REM sleep comes an increase in rebound REM sleep time on dry land to make up for quality sleep loss (Venancio and Suchecki, 2015). This study (by Oleg I. Lyamin et al., 2018) aimed to show that as fur seals spend their time hunting in seawater, they go long time spans with greatly reduced REM sleep and minimal rebound periods when returning to “baseline conditions”, or dry land. It was hypothesized that, since REM sleep was originally thought to be homeostatically regulated, it may actually instead serve to undo the effects that bilateral non-REM sleep has on the brain, including a reversal of reduced brain temperature and metabolism effects. This information can also prove useful in explaining the absence of REM sleep in other cetaceans, such as whales and dolphins.
This study was carried out on four juvenile northern fur seals that were captured on the Commander Islands in the Western Pacific near Russia and then transported to the Utrish Marine Station of the Severtsov Institute in the Black Sea. Various electrodes and wires were surgically implanted into the seals to measure various aspects of the seal’s brain, eyes, and neck muscles, giving researchers the ability to record REM sleep. Once the study began, each seal was tested over 2 baseline days on “dry land”, followed by 10-14 “in seawater” days, immediately followed by 2 “recovery days”. Sleep position was also noted, as it was interesting to see if there was a correlation between body positioning and sleep time (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Various sleeping positions in fur seals. These body positions help researchers identify types of sleep and how long the seal is sleeping, as it can sometimes be hard to visualize. (Oleg I. Lyamin et al., 2018 and Oleg I. Lyamin et al. 2017)
Results show that, when in water, the daily average of REM sleep time in the seals was 3 minutes, which was greatly reduced from the average of 80 minutes on dry land. The number of REM sleep episodes overall also decreased in water, dropping to 13% of baseline conditions. In total, the accumulated loss of REM sleep was 765 minutes below projected baseline amounts. Once returned to dry land, it was expected that the seals would sleep for long periods of time to make up for lost sleep. However, results showed that the amounts of REM sleep were not significantly greater when compared to baseline data (Figures 2 and 3). All of these results confirm the statement that when in seawater, fur seals greatly reduce the amount of REM sleep, followed by minimal rebound to accommodate sleep loss.

Figure 2: Comparison of REM sleep times and episodes to SWS and BSWS. REM sleep is suppressed majorly when the seals enter the water for days at the time with very little rebound after returning to dry land. (Oleg I. Lyamin et al., 2018)
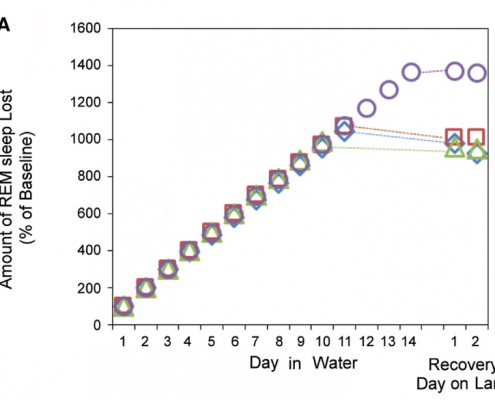
Figure 3: Total percentage of REM sleep lost in comparison to baseline conditions on dry land. Again, there was very little, if any, rebound shown to recover after going many days with suppressed REM sleep. (Oleg I. Lyamin et al., 2018)
Overall, this study presents the ability of northern fur seals to be able to adjust their REM sleep schedules in water in their favor. This long closure of the eyes would eliminate the ability to see incoming attacks and would put them at a disadvantage. Also, thermoregulation is flawed during REM sleep, so the seals could potentially expose themselves to hypothermia (Parmeggiani et al., 1977). Instead, the researchers concluded that the seals perform unihemispheric nonREM sleep, which ultimately allows half of the brain to rest while the other half is alert. Further studies are encouraged to determine the relationship of this pattern among several marine species and to record temperature from both cerebral halves of the brain to better understand this ability in these mammals.
Works Cited
Kushida, C.A., Bergmann, B.M., and Rechtschaffen, A. (1989). Sleep deprivation in the rat: IV. Paradoxical sleep deprivation. Sleep 12, 22–30.
Lyamin, O.I., Mukhametov, L.M., and Siegel, J.M. (2017). Sleep in the northern fur seal. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 44, 144–151.
Lyamin, Oleg I., et al. “Fur seals suppress REM sleep for very long periods without subsequent rebound.” Current Biology (2018).
Parmeggiani, P.L., Zamboni, G., Cianci, T., and Calasso, M. (1977). Absence of thermoregulatory vasomotor responses during fast wave sleep in cats. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 42, 372–380.
Venancio, D.P., and Suchecki, D. (2015). Prolonged REM sleep restriction induces metabolic syndrome-related changes: mediation by pro-inflam- matory cytokines. Brain Behav. Immun. 47, 109–117.